Air Power • Stealth Fighters
Related reading: DRDO’s Key Defence Projects • HAL and India’s Fighter Production • Tejas Mk2 Explained
Why India Needs AMCA
Today the IAF flies a mixed fleet of Su-30MKI, Rafale, Mirage-2000, MiG-29, and LCA Tejas. AMCA will add a stealthy, multirole spearhead to that mix.
Development Timeline
- Concept & Pre-design: Early 2010s.
- Preliminary design & testing: Mid-to-late 2010s.
- Prototype phase: Targeted this decade with flight testing to follow.
- Series production: Planned after certification; Mk-2 follows with an indigenous engine.
Key Features
Stealth
Internal weapons bays, aligned edges, and composites aim to reduce radar cross-section. Shaping and coatings work together to manage signature.
Engines & Supercruise
Mk-1 is planned around the GE F414 class. Mk-2 targets a higher-thrust indigenous powerplant. Supercruise is a design goal for sustained supersonic flight without afterburner.
Sensors & Avionics
An AESA radar, IRST, electronic warfare suite, and sensor fusion give the pilot a unified picture. Data-links enable networked combat with manned and unmanned assets.
Weapons
AMCA is designed to carry Astra class BVRAAMs and precision-guided munitions internally. Future plans include BrahMos-NG and stand-off weapons for deep strike.
Planned Variants
- AMCA Mk-1: Stealth airframe with imported engines; rapid induction focus.
- AMCA Mk-2: Greater use of composites, higher thrust, expanded mission systems.
AMCA vs Other 5th-Generation Fighters
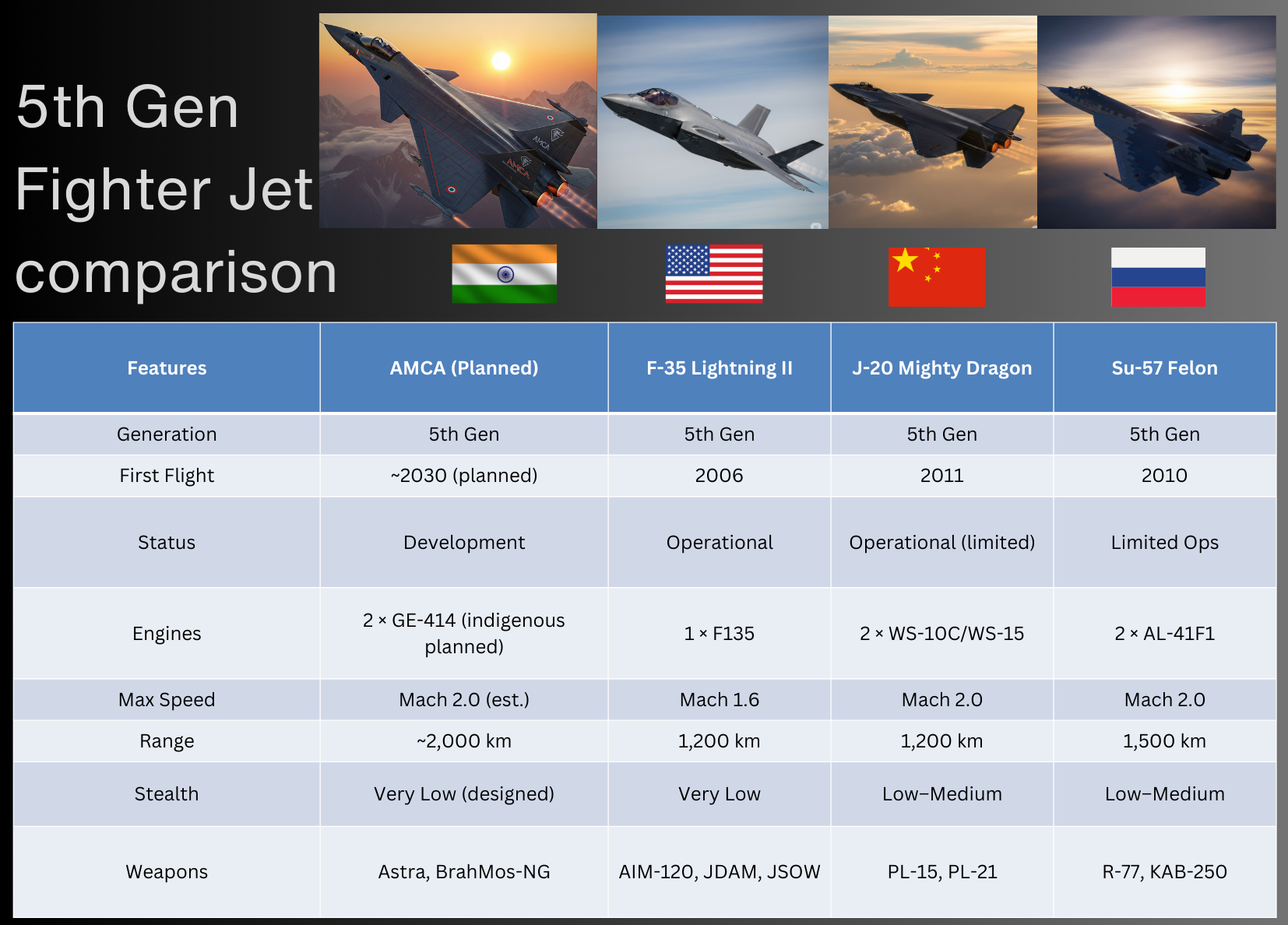
Challenges Ahead
- Engine maturity. Indigenous high-thrust development is complex. India has announced to co-develop a new 120 kN engine with French aerospace major Safran.
- Funding & schedules. Big aerospace programs need steady investment and governance.
- Production scale. On-time delivery and quality control are critical.
- Supply chain depth. Materials, avionics, and precision manufacturing must grow locally.
Strategic Importance
AMCA strengthens deterrence, improves first-day-of-war options, and pushes India’s aerospace ecosystem forward. It also opens doors for exports in the long term and inspires the next generation of engineers.
Future Outlook
By the mid-2030s, the IAF could field a balanced mix: Tejas Mk-2, Rafale, Su-30MKI upgrades, AMCA Mk-1/Mk-2, and loyal-wingman drones like Ghatak UCAV. AMCA sits at the core of that plan.
FAQs
Is AMCA a stealth aircraft?
Yes. The airframe uses shaping, coatings, and internal bays to manage signatures. The design targets low observability from the outset.
Will AMCA carry BrahMos-NG?
It is a goal for future blocks. The smaller form factor of BrahMos-NG makes internal or semi-recessed carriage more practical.
How is AMCA different from Tejas?
Tejas vs AMCA: Tejas is a lightweight 4.5-gen fighter. AMCA is a medium-class 5th-gen stealth platform with internal weapons and advanced fusion.


Pingback: Tejas Mk2: India’s Next-Generation Fighter Jet Explained - DefenceNiti.com
Pingback: Inside the AMCA Program: Development Timeline and Key Milestones - DefenceNiti.com
Pingback: AMCA Stealth Technology: India’s Leap into Low Observability Warfare - DefenceNiti.com
Pingback: AMCA Engine Development: Powering India’s 5th Gen Fighter - DefenceNiti.com
Pingback: L&T and BEL Enter AMCA Race: Transforming India’s 5th-Gen Fighter Program — DefenceNiti - DefenceNiti.com
Pingback: AMCA: India’s 5th Generation Fighter – The Complete Guide - DefenceNiti.com
Pingback: AI and Quantum Computing in Indian Military Applications - DefenceNiti.com
Pingback: Rise of Unmanned Aerial Systems: Drones in Indian Defence - DefenceNiti.com